2012年ACCA考试《F3财务会计》讲义辅导(1)
☆Types of business entity
A business can be organized in one of the several ways:
●Sole trader– a business owned and operated by one person.
The simple form of business is the sole trader. This is owned and managed by one person, although there might be any number of employees. A sole trader is fully personally liable for any losses that the business might make.
●Partnership– a business owned and operated by two or more people.
A partnership is a business owned jointly by a number of partners. The partners are jointly and severely liable for any losses that the business might make.
(Traditionally the big accounting firms have been partnerships, although some are converting their status to limited liability companies.)
●Limited Liability Company– a business owned by many people and operated by many ( though not necessarily the same) people. Companies are owned by shareholders. Shareholders are also known as members. As a group, they elect the directors who run the business. Companies are always limited companies.
In summary, types of business entity should be differentiated in Ownership; Operation right and Liability for the business to undertake.
For all three types of entity, the money put up by the individual, the partners or the shareholders, is referred to as the business capital. In the case of a company, this capital is divided into shares.
☆Business Transactions: Main types of business transactions for a business include:
●Purchase of inventory for resale
●Sales of goods
●Purchase of non-current assets
●Payment of expenses
●Introduction of new capital to the business
●Withdrawal of funds from the business by the owner
☆Cash and credit transactions:
Cash transactions: the buyer pays for the item immediately or possibly in advance.
Credit transactions: the buyer does not have to pay for the item on receipt, but is allowed some time ( a credit period) before having to make the payment.
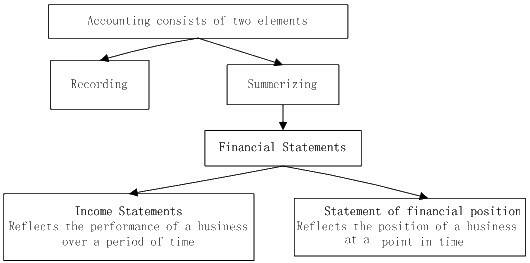
☆Definition of accounting
Recording : transactions must be recorded as they occur in order to provide up-to-date information for management.
Summarizing: the transactions for a period are summarized in order to provide information about the company to interested parties.
☆Types of accounting
Financial accounting vs management accounting
|
|
Financial accounting |
Cost and management |
|
Purpose |
Record financial |
Information of cost |
|
Legal requirement |
Limited liability company, |
No legal requirement |
|
Main user |
External |
Internal |
|
Time |
At the end of period |
regularly |
|
Information |
historic |
historic and forecast |
☆Users of financial statements
Accounting reports users include:
●Management: Need information about the company’s financial situation as it is currently and it is expected to be in the future. This is to enable them to manage
the business efficiently and to make effective decisions.
●Investors: The providers of risk, capital and their advisers are concerned with the risk inherent in, and return provided by, their investments. They need information to help them determine whether they should buy, hold or sell.
●Trade payables/ Suppliers:Suppliers and other trade payables. Suppliers and other trade payables are interested in information that enables them to determine whether amounts owing to them will be paid when due. Trade payables are likely to be interested in an enterprise over a shorter period than lenders unless they are dependent upon the continuance of an enterprise as a major customer.
●Shareholders: Shareholders are also interested in market value of shares as well as information which enables them to assess the ability of the enterprise to pay dividends.
●Lenders: Lenders are interested in information that enables them to determine whether their loans, and the interest attaching to them, will be paid when due.
●Customers: Customers have an interest in information about the continuance of an enterprise, especially when they have a long term involvement with or are dependent on, the enterprise.
●Government and their agencies: Governments are their agencies are interested in the allocation of resources and, therefore, the activities of enterprises. They also require information in order to regulate the activities of enterprises, determine taxation policies and as the basis for national income and similar statistics.
●Employees: Employees and their representative groups are interested in information about the stability and profitability of their employers. They are also interested in information which enables them to assess the ability of the enterprise to prove remuneration, retirement benefits and employment opportunities.
●General public: Enterprises affect members of the public in an variety of ways. For example, enterprises may make a substantial contribution to the local economy in many ways including the number of people they employ and their patronage of local suppliers. Financial statements may assist the public by providing information about the trends and recent developments in the prosperity of the enterprise and the range of its activities.
☆The business entity concept
The business entity concept
●States that financial accounting information relates only to the activities of the business entity and not to the activities of its owner.
●The business entity is treated as separate from its owners.

相关阅读
ACCA考试中的F3考试学习技巧2013/08/07
ACCA考试中的F1考试学习技巧2013/08/07
2012年12月ACCA考试F4考试考官报告2013/06/19